Lifestyle
Sharp vision: New glasses help the legally blind see
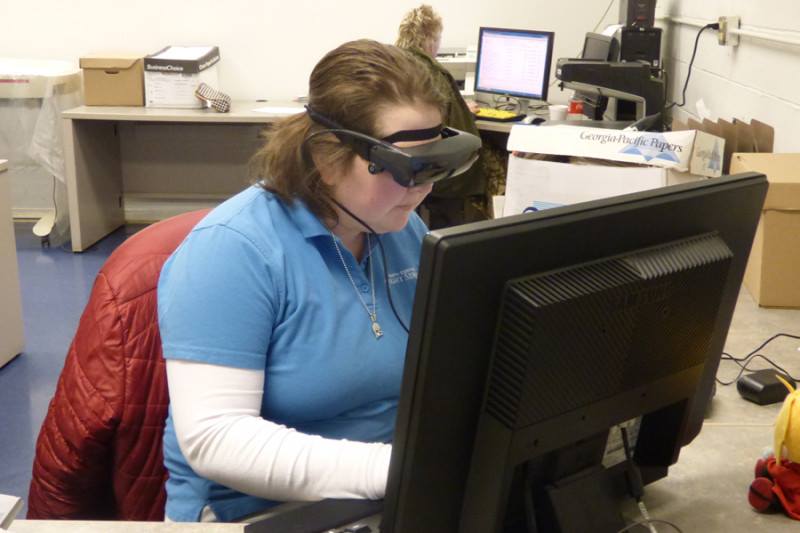

The headsets from eSight transmit images from a forward-facing camera to small internal screens — one for each eye — in a way that beams the video into the wearer’s peripheral vision. (Photo: eSight Corp/Facebook)
SAN FRANCISCO—Jeff Regan was born with underdeveloped optic nerves and had spent most of his life in a blur. Then four years ago, he donned an unwieldy headset made by a Toronto company called eSight.
Suddenly, Regan could read a newspaper while eating breakfast and make out the faces of his co-workers from across the room. He’s been able to attend plays and watch what’s happening on stage, without having to guess why people around him were laughing.
“These glasses have made my life so much better,” said Regan, 48, a Canadian engineer who lives in London, Ontario.
The headsets from eSight transmit images from a forward-facing camera to small internal screens — one for each eye — in a way that beams the video into the wearer’s peripheral vision. That turns out to be all that some people with limited vision, even legal blindness, need to see things they never could before. That’s because many visual impairments degrade central vision while leaving peripheral vision largely intact.
Although eSight’s glasses won’t help people with total blindness, they could still be a huge deal for the millions of peoples whose vision is so impaired that it can’t be corrected with ordinary lenses.
EYE TEST
But eSight still needs to clear a few minor hurdles.
Among them: proving the glasses are safe and effective for the legally blind. While eSight’s headsets don’t require the approval of health regulators — they fall into the same low-risk category as dental floss — there’s not yet firm evidence of their benefits. The company is funding clinical trials to provide that proof.
The headsets also carry an eye-popping price tag. The latest version of the glasses, released just last week, sells for about $10,000. While that’s $5,000 less than its predecessor, it’s still a lot for people who often have trouble getting high-paying jobs because they can’t see.
Insurers won’t cover the cost; they consider the glasses an “assistive” technology similar to hearing aids.
ESight CEO Brian Mech said the latest improvements might help insurers overcome their short-sighted view of his product. Mech argues that it would be more cost-effective for insurers to pay for the headsets, even in part, than to cover more expensive surgical procedures that may restore some sight to the visually impaired.
NEW GLASSES
The latest version of ESight’s technology, built with investments of $32 million over the past decade, is a gadget that vaguely resembles the visor worn by the blind “Star Trek” character Geordi La Forge, played by LeVar Burton.
The third-generation model lets wearers magnify the video feed up to 24 times, compared to just 14 times in earlier models. There’s a hand control for adjusting brightness and contrast. The new glasses also come with a more powerful high-definition camera.
ESight believes that about 200 million people worldwide with visual acuity of 20/70 to 20/1200 could be potential candidates for its glasses. That number includes people with a variety of disabling eye conditions such as macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, ocular albinism, Stargardt’s disease, or, like Regan, optic nerve hypoplasia.
So far, though, the company has sold only about 1,000 headsets, despite the testimonials of wearers who’ve become true believers.
Take, for instance, Yvonne Felix, an artist who now works as an advocate for eSight after seeing the previously indistinguishable faces of her husband and two sons for the first time via its glasses. Others, ranging from kids to senior citizens, have worn the gadgets to golf, watch football or just perform daily tasks such as reading nutrition labels.
EYING THE COMPETITION
ESight isn’t the only comany focused on helping the legally blind. Other companies working on high-tech glasses and related tools include Aira, Orcam, ThirdEye, NuEyes and Microsoft.
But most of them are doing something very different. While their approaches also involve cameras attached to glasses, they don’t magnify live video. Instead, they take still images, analyze them with image recognition software and then generate an automated voice that describes what the wearer is looking at — anything from a child to words written on a page.
Samuel Markowitz, a University of Toronto professor of ophthalmology, says that eSight’s glasses are the most versatile option for the legally blind currently available, as they can improve vision at near and far distances, plus everything in between.
Markowitz is one of the researchers from five universities and the Center for Retina and Macular Disease that recently completed a clinical trial of eSight’s second-generation glasses. Although the results won’t be released until later this year, Markowitz said the trials found little risk to the glasses. The biggest hazard, he said, is the possibility of tripping and falling while walking with the glasses covering the eyes.
The device “is meant to be used while in a stationary situation, either sitting or standing, for looking around at the environment,” Markowitz said.