Business and Economy
Energy Consumption in the Philippines
In recent years, the Philippine economy continues to boom. Together with this growth is the increase in supply and demand across sectors. Focusing on the energy sector of the country, despite conventional energy consumption dropping, the move to renewable energy sources projects increase in the near future’s consumption.
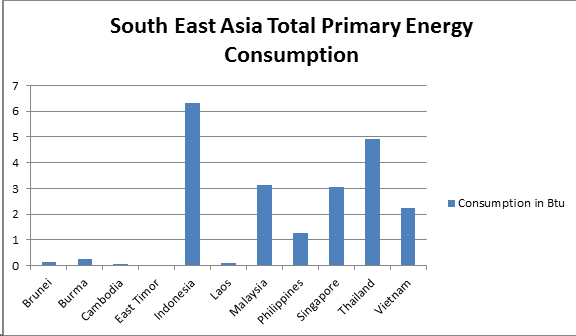
According to the International Energy Statistics (IES) latest study on Philippine energy consumption, the total primary energy usage of the country reaches roughly 1.260 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu). This amount shows that the country’s energy consumption level is drastically low as it barely makes up 1 percent of the total 199 Btu total energy consumed by Asia and Oceania. However in Southeast Asia, the Philippines is positioned at the median of countries in terms of energy utilization.
Concurrently, the Philippines has started to prefer renewable sources. Natural gas often used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation is consumed at 102.41 billion cubic feet. This amount is higher from the previous year’s 99.09 billion cubic feet.
Petroleum, which is commonly refined into various types of fuels, on the other hand, totaled to 308.44 thousand barrels consumed per day. This is lower to last year’s 321.68 thousand barrels per day. Likewise, coal, which is demanded in power plants, reached 15.408 million short tons consumed. This is lower from the previous year’s 18.103 million short tons.
Electricity, which is usually used for lighting, is consumed at 58.33 billion kilowatt-hours. Aside from lighting, electricity is also used for telecommunications and transportation. But despite seemingly high demand in the electricity market, its consumption lowered from last year’s 61.31 billion kilowatt-hours.
Other energies consumed by the country in significant amounts are net hydroelectric, nuclear, and geothermal, solar, wind and wood, and waste electricity.
As for local studies, total energy consumed and most commonly used energies differed per sector.
Residential Energy Consumption
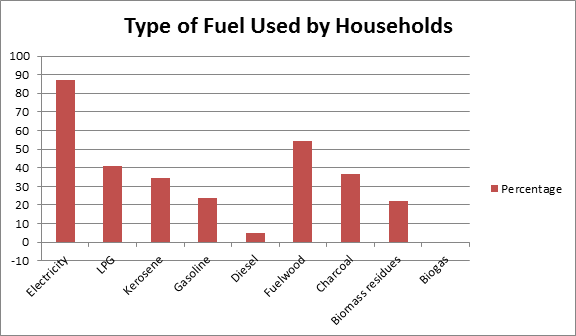
According to the results of the latest National Statistics Office (NSO) and Department of Energy (DOE) Household Energy Consumption Survey (HECS), Philippine households commonly used electricity as their main source of energy. During the reference period March to August 2011, 18 million households or 87.2 percent of the 21 million participating households used electricity. This is followed by fuelwood, LPG, charcoal, kerosene, gasoline, biomass residues with and diesel as household sources of energy.
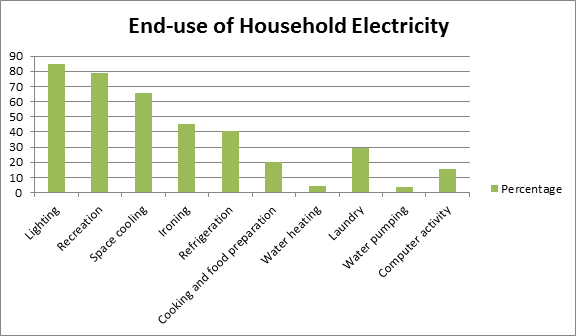
Electricity was most commonly used for lighting purposes with about 74 percent of the households reporting its use. Electricity was also used for recreation with 78.7 percent of households using it for listening to radio, watching television, singing in the karaoke or playing video games. The other uses of electricity were for space cooling, ironing, refrigeration, cooking and food preparation, water heating, laundry, water pumping and computer activity.
Non-conventional energies were utilized for the same purposes. Fuelwood was most commonly used for cooking and heating water with 54.2 percent and 20.1 percent of households. Charcoal was also utilized for cooking with 35.3 percent. And though less preferred, biomass residues were used for similar purposes with less than 0.1 percent.
Among the petroleum products, LPG came after fuelwood for cooking purposes with 40.5 percent. Kerosene came after electricity for lighting with 30.3 percent. Gasoline, on the other hand, was the top source of energy for vehicles with 88.4 percent. Next to gasoline was diesel with 15.6 percent.
Wherein electricity was the most common source of energy used by Filipino households, local establishments favored a different energy source.
Industrial and Commercial Energy Consumption
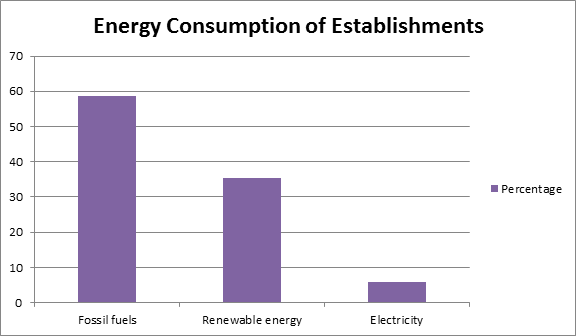
Based from the results of the first National Statistics Office (NSO) and Department of Energy (DOE) Survey of Energy Consumption of Establishments (SECE) conducted in 2010, a total of 53,889.59 kilo Tons of oil equivalent (kToe) were consumed by 143,868 energy-consuming industries. This was comprised of fossil fuels with 31,634.83 kToe consumed, renewable energy with 19,118.70 kToe, and electricity with 3,136.67 kToe.
From the recorded total quantity of fossil fuels consumed by establishments, coal was the most commonly used reaching 20,227.57 kToe. Almost all quantity of coal or 99.8 percent was used to run machineries and equipment while the remaining 0.2 percent was used as raw material and for other non-energy use. Next to coal were petroleum products including gasoline, diesel, fuel, bunker oil, kerosene, LPG, AVGAS, AVTURBO, and asphaltin, which totaled 3,854.23 kToe. Natural gas was also consumed by establishments as approximately 1,116.42 kToe were used to run transport equipment.
For renewable energy, on the other hand, fuelwood registered at 691.30 kToe. Charcoal was also consumed with 60.09 kToe for the same purposes. Other biomass fuels consisting of bagasse, biogas, sawdust, rice, coconut and corn derivation made up 18,367.30 kToe. All renewable energies were used to run machineries and equipments.
Contrary to the residential sector, electricity consumption on the industrial and commercial sectors was the least of all energy sources. Its total quantity reached only 3,136.67 kToe.
Establishments included in the survey were under agriculture, manufacturing, construction, trade, food service, information, communication, insurance, real estate, education, health, arts, entertainment and recreation among other product and service industries.
In the coming years, Philippine energy consumption levels may considerably change as the national government starts resource developments and implements market reforms in the power sector to achieve energy efficiency and economic growth.






















Pingback: Natural Crisis | c32jgmendoza
joan Doblon
August 10, 2016 at 9:29 PM
1. Energy sources
We have so many energy sources these are the hydroelectric, nuclear and geothermal, solar, wind and waste electricity but here in the Philippines, we used electricity as a source of energy, telecommunications, and transportation. And electricity plays an important role in human lives because of its advancements it brought humans satisfaction.
2. Consumers
According to surveys, electricity was the commonly used source of energy in the Philippines. And as the year passed by the people find some alternative sources of energy and uses some types of fossil fuels to serve as a substitute to electricity and to prevent the consumer from consuming energy too much.
3. Consumption
As the years passed by the Industrial and Commercial Establishments uses fossil fuels as a source of their energy most of their machines and equipment’s were operated and run by fossil fuels. In the next generation, our dependency on electricity will be changed and our consumption will also follow.
Here are the ways on how to mitigate the Energy crisis.
1. Reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources.
2. Buy energy efficient products
3. Energy simulation
4. Finding alternative means
5. Use energy efficiently