Lifestyle
Superagers’ youthful brains offer clues to keeping sharp
WASHINGTON — It’s pretty extraordinary for people in their 80s and 90s to keep the same sharp memory as someone several decades younger, and now scientists are peeking into the brains of these “superagers” to uncover their secret.
The work is the flip side of the disappointing hunt for new drugs to fight or prevent Alzheimer’s disease.
Instead, “why don’t we figure out what it is we might need to do to maximize our memory?” said neuroscientist Emily Rogalski, who leads the SuperAging study at Northwestern University in Chicago.
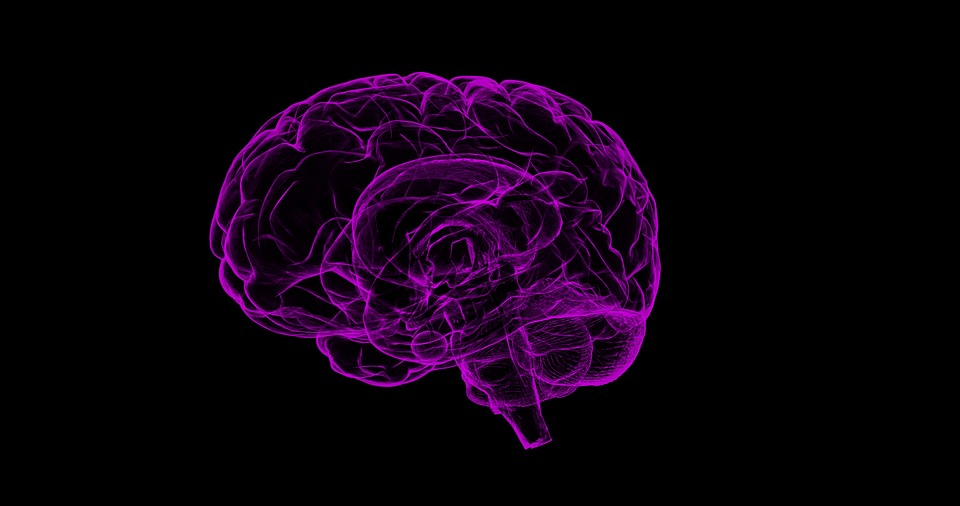
Parts of the brain shrink with age, one of the reasons why most people experience a gradual slowing of at least some types of memory late in life, even if they avoid diseases like Alzheimer’s.
But it turns out that superagers’ brains aren’t shrinking nearly as fast as their peers’. And autopsies of the first superagers to die during the study show they harbour a lot more of a special kind of nerve cell in a deep brain region that’s important for attention, Rogalski told a recent meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
These elite elders are “more than just an oddity or a rarity,” said neuroscientist Molly Wagster of the National Institute on Aging, which helps fund the research. “There’s the potential for learning an enormous amount and applying it to the rest of us, and even to those who may be on a trajectory for some type of neurodegenerative disease.”
What does it take to be a superager? A youthful brain in the body of someone 80 or older. Rogalski’s team has given a battery of tests to more than 1,000 people who thought they’d qualify, and only about 5 per cent pass. The key memory challenge: Listen to 15 unrelated words, and a half-hour later recall at least nine. That’s the norm for 50-year-olds, but the average 80-year-old recalls five. Some superagers remember them all.
“It doesn’t mean you’re any smarter,” stressed superager William “Bill” Gurolnick, who turns 87 next month and joined the study two years ago.
Nor can he credit protective genes: Gurolnick’s father developed Alzheimer’s in his 50s. He thinks his own stellar memory is bolstered by keeping busy. He bikes, and plays tennis and water volleyball. He stays social through regular lunches and meetings with a men’s group he co-founded.
“Absolutely that’s a critical factor about keeping your wits about you,” exclaimed Gurolnick, fresh off his monthly gin game.
Rogalski’s superagers tend to be extroverts and report strong social networks, but otherwise they come from all walks of life, making it hard to find a common trait for brain health. Some went to college, some didn’t. Some have high IQs, some are average.
She’s studied people who’ve experienced enormous trauma, including a Holocaust survivor; fitness buffs and smokers; teetotallers and those who tout a nightly martini.
But deep in their brains is where she’s finding compelling hints that somehow, superagers are more resilient against the ravages of time.
Early on, brain scans showed that a superager’s cortex — an outer brain layer critical for memory and other key functions — is much thicker than normal for their age. It looks more like the cortex of healthy 50- and 60-year-olds.
It’s not clear if they were born that way. But Rogalski’s team found another possible explanation: A superager’s cortex doesn’t shrink as fast.
Over 18 months, average 80-somethings experienced more than twice the rate of loss.
Another clue: Deeper in the brain, that attention region is larger in superagers, too. And inside, autopsies showed that brain region was packed with unusual large, spindly neurons — a special and little understood type called von Economo neurons thought to play a role in social processing and awareness.
The superagers had four to five times more of those neurons than the typical octogenarian, Rogalski said — more even than the average young adult.
The Northwestern study isn’t the only attempt at unraveling long-lasting memory.
At the University of California, Irvine, Dr. Claudia Kawas studies the oldest-old, people 90 and above. Some have Alzheimer’s. Some have maintained excellent memory and some are in between.
About 40 per cent of the oldest-old who showed no symptoms of dementia in life nonetheless have full-fledged signs of Alzheimer’s disease in their brains at death, Kawas told the AAAS meeting.
Rogalski also found varying amounts of amyloid and tau, hallmark Alzheimer’s proteins, in the brains of some superagers.
Now scientists are exploring how these people deflect damage. Maybe superagers have different pathways to brain health.
“They are living long and living well,” Rogalski said. “Are there modifiable things we can think about today, in our everyday lives” to do the same?