Breaking
Tillerson says China asked North Korea to stop nuclear tests
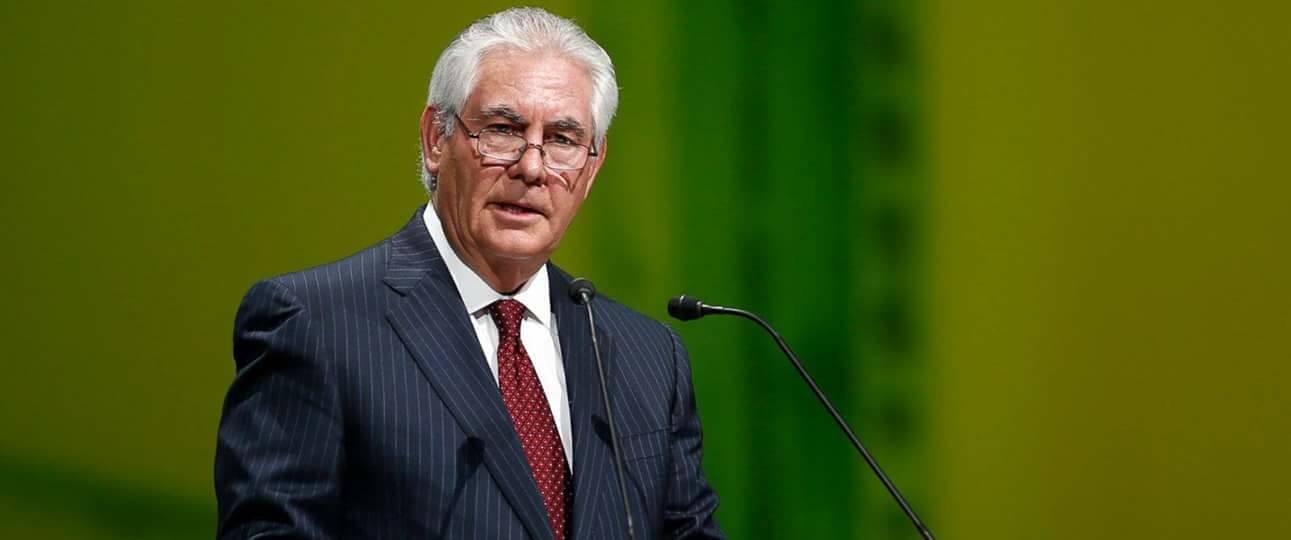

U.S. Secretary of State Rex Tillerson said Thursday that China has threatened to impose sanctions on North Korea if it conducts further nuclear tests. (Photo; Rex Tillerson Secretary/Facebook)
WASHINGTON — U.S. Secretary of State Rex Tillerson said Thursday that China has threatened to impose sanctions on North Korea if it conducts further nuclear tests.
“We know that China is in communications with the regime in Pyongyang,” Tillerson said on Fox News Channel. “They confirmed to us that they had requested the regime conduct no further nuclear test.”
Tillerson said China also told the U.S. that it had informed North Korea “that if they did conduct further nuclear tests, China would be taking sanctions actions on their own.”
Earlier Thursday, the senior U.S. Navy officer overseeing military operations in the Pacific said the crisis with North Korea is at the worst point he’s ever seen, but he declined to compare the situation to the Cuban missile crisis decades ago.
“It’s real,” Adm. Harry Harris Jr., commander of U.S. Pacific Command, said during testimony before the Senate Armed Services Committee.
Harris said he has no doubt that North Korean leader Kim Jong Un intends to fulfil his pursuit of a nuclear-tipped missile capable of striking the United States. The admiral acknowledged there’s uncertainty within U.S. intelligence agencies over how far along North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs are. But Harris said it’s not a matter of if but when.
“There is no doubt in my mind,” Harris said.
China’s foreign ministry had no immediate comment on Tillerson’s remarks on new sanctions, but a spokesman Thursday said Beijing remained committed to implementing sanctions imposed under U.N. Security Council resolutions.
“And the reason that China implements relevant resolutions is to fulfil our due international obligation rather than being pressured by any outside parties,” Geng Shuang said at a daily briefing.
China has consistently called for an end to North Korea’s nuclear weapons program, but says it opposes unilateral sanctions imposed without a U.N. mandate. China in January suspended coal imports from the North for the rest of the year, but it did so following the passage of a Security Council resolution capping Pyongyang’s coal exports.
Other economic activity with North Korea remains robust.
Still, Beijing has been increasing pressure on North Korea, and would be willing to impose punitive measures unilaterally in the event of another nuclear test, said Cheng Xiaohe, an associate professor at Renmin University’s School of International Studies in Beijing.
“So Tillerson’s comments are correct — but be careful, China does so for China’s national interest, not as a result of U.S. pressure,” Cheng said.
The Trump administration has declared that all options, including a targeted military strike, are on the table to block North Korea from carrying out threats against the United States and its allies in the region. But a pre-emptive attack isn’t likely, U.S. officials have said, and the administration is pursuing a strategy of putting pressure on Pyongyang with assistance from China, North Korea’s main trading partner and the country’s economic lifeline.
With international support, the Trump administration said Thursday it wants to exert a “burst” of economic and diplomatic pressure on North Korea that yields results within months to push the communist government to change course from developing nuclear weapons.
Susan Thornton, the acting top U.S. diplomat for East Asia, said there’s debate about whether Pyongyang is willing to give up its weapons programs. She said the U.S. wants “to test that hypothesis to the maximum extent we can” for a peaceful resolution.
But signalling that military action remains possible, Thornton told an event hosted by the Foundation for Defence of Democracies — the Washington think-tank has advocated tougher U.S. policies on Iran and North Korea — that the administration treats North Korea as its primary security challenge and is serious that “all options are on the table.”
“We are not seeking regime change and our preference is to resolve this problem peacefully,” Thornton said, “but we are not leaving anything off the table.”
Tillerson took a similar stand in the Fox News interview Thursday, saying: “We do not seek regime change in North Korea. … What we are seeking is the same thing China has said they seek — a full denuclearization of the Korean peninsula.”
In a separate interview with National Public Radio, Tillerson said the U.S. remains open to holding direct negotiations with North Korea.
“But North Korea has to decide they’re ready to talk to us about the about the right agenda, and the right agenda is not simply stopping where they are for a few more months or a few more years and then resuming things,” he said, according to excerpts of an interview that will air Friday morning. “That’s been the agenda for the last 20 years.”
Multi-nation negotiations with North Korea on its nuclear program stalled in 2008. The Obama administration attempted to resurrect them in 2012, but a deal to provide food aid in exchange for a nuclear freeze soon collapsed.
The House GOP leadership announced late Thursday that it would vote next week on new sanctions against North Korea that would target its shipping industry and those who employ North Korean slave labour abroad.
“The time for waiting on North Korea to get its act together is over. Congress has led the effort to institute tough and far-reaching sanctions against Pyongyang,” said House Majority Leader Kevin McCarthy, R-Calif.
In a show of military might, the U.S. has sent a massive amount of American weaponry to the region. A group of American warships led by the aircraft carrier USS Carl Vinson is in striking range of North Korea “if the president were to call on it,” Harris told the committee. A U.S. missile defence system called Terminal High-Altitude Area Defence is being installed in South Korea.
Harris said he has adequate forces to “fight tonight” against North Korea if that were to become necessary.